InfiniBand: The Future Standard of High-Performance Computing

Over the past decades, InfiniBand and Ethernet continued to compete delivering the best features to end users.
As the most widely used network protocol in the market, Ethernet has several advantages, including its compatibility with most devices and its cost advantage.
However, as the Internet today has grown into a large infrastructure that provides various data intensive applications, organizations are establishing data centers to address the needs of dependable computing of the explosive volume of data.
Here are the reasons why InfiniBand stands out from the competition:
Highly efficient and low latency.
InfiniBand is the most efficient network protocol.Because of its architecture, InfiniBand delivers exceptional throughput and low latency, it incorporates processing engines inside the network that accelerate data processing for deep learning and high-performance computing.
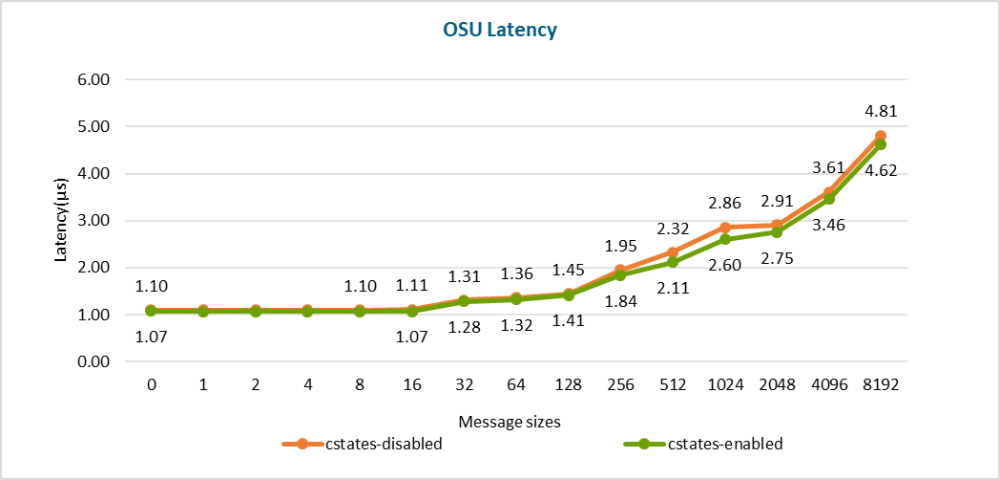
InfiniBand latency with switch
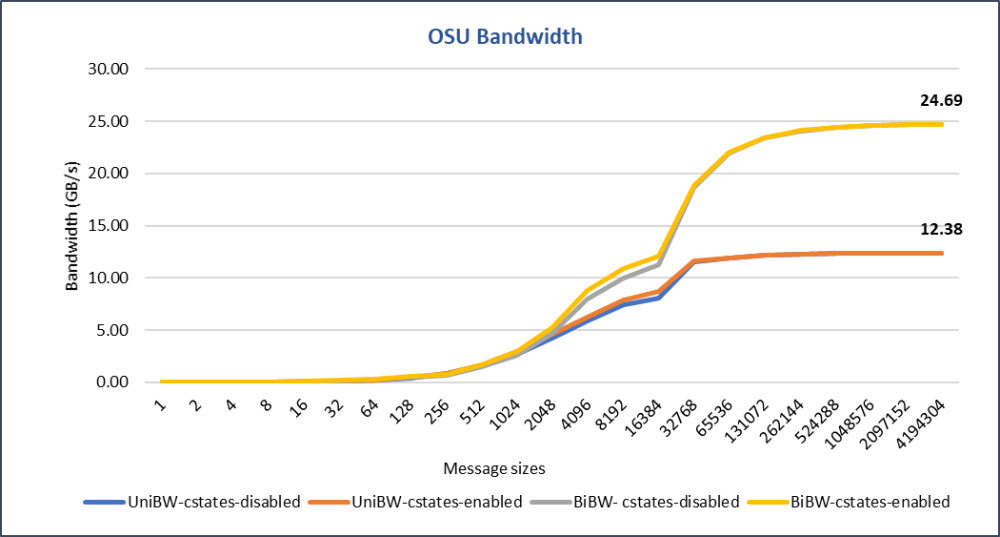
InfiniBand latency with switch
Source:DELL Technologies
Scalability
InfiniBand has a highly scalable architecture. It can support thousands of nodes within a single subnet and could also be extended through InfiniBand routers to create nearly unlimited cluster sizes.
On the opposite, Ethernet has its limitations regarding expandability due to its nature. Additional routers, switches and many meters of wires are needed for network expansion and the speed is limited.
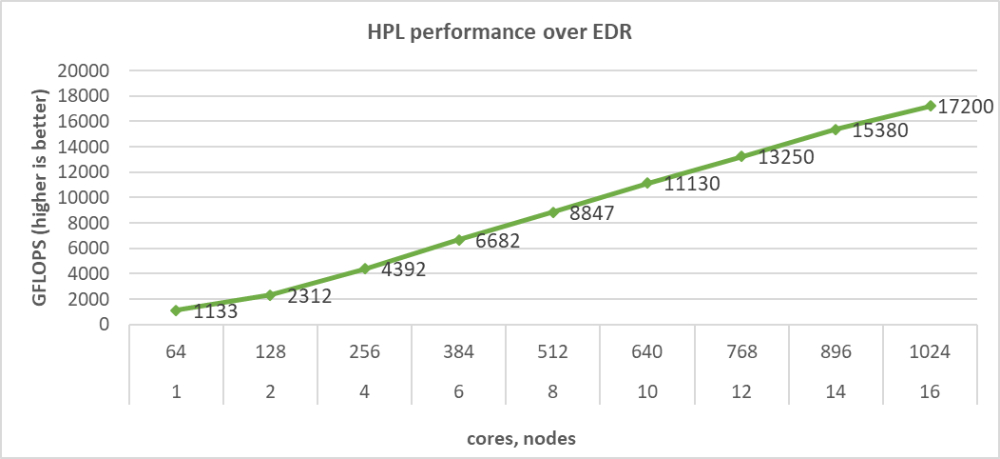
HPL across 16 servers
Source:DELL Technologies
RDMA
InfiniBand supports RDMA (Remote Direct Memory Access), a technology that allows users directly access the virtual memory on remote computers. The RDMA technology provides low latency through stack bypass and copy avoidance, reduces CPU utilization, memory bandwidth bottlenecks and provides high bandwidth utilization.
The above reasons make InfiniBand the dominant technology in the field of high-performance computing (HPC), deep-learning infrastructures, and hyperscale cloud data centers.
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |
|---|---|---|
| Ethernet |
|
|
| InfiniBand |
|
|
The lead player in the InfiniBand market: Mellanox
Major players in the InfiniBand market include Mellanox and Intel. Mellanox, now a part of NVIDIA group, is the leading brand of InfiniBand semiconductors, providing complete solutions including switches, host channel adapters, and target channel adapters to the server, communications, data storage, and embedded markets.
More and more HPC users are choosing Mellanox's InfiniBand network because its strong scalability and compatibility with all kinds of chipsets, such as X86, ARM, POWER and GPU.
Nextron is honored to be part of this trend of continuous pursuit of future interconnect solutions. The performance and quality of InfiniBand I/O connectors series have been recognized for several years.
Related products including QSFP+, QSFP28 and QSFP-DD are crafted with Nextron’s great understanding of InfiniBand protocol. SFP products can be used for both InfiniBand and Ethernet.
| Name | Abbreviation | Raw Signling Rate | Applied Encoding | Effective Data Rate | Aggregated(4x) Throughput | module |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Data Rate | SDR | 2.5Gb/s | 8b/10b | 2Gb/s | 8Gb/s | CX4/SFF-8470 |
| Double Data Rate | DDR | 5Gb/s | 8b/10b | 4Gb/s | 16Gb/s | CX4/SFF-8470 |
| Quad Data Rate | QDR | 10Gb/s | 8b/10b | 8Gb/s | 32Gb/s | QSFP+ |
| Fourteen Data Rate | FDR | 14.1Gb/s | 64b/66b | 13.64Gb/s | 54.5Gb/s | QSFP+ |
| Enhanced Data Rate | EDR | 25.8Gb/s | 64b/66b | 25Gb/s | 100Gb/s | QSFP28 |
| High Data Rate | HDR | 51.6Gb/s | 64b/66b | 50Gb/s | 200Gb/s | QSFP DD |
| Next Data Rate | NDR | TBD | TBD | TBD | TBD | TBD |
InfiniBand Related Products
Products for InfiniBand and Ethernet
The quality of Nextron’s InfiniBand I/O connectors is proven by great market results. Contact our team marketing@nextron.com.tw for more details.